Main page
About us
Sliding Bearings Consulting
Advertising Opportunities

to Fluids
to Lubricants
Graphite as solid lubricant
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
Graphite is a crystalline, low density and soft allotrope of carbon.
Graphite is a solid lubricant relating to the class of Inorganic lubricants with lamellar structure, which also includes molybdenum disulphide, boron nitride and some other sulphides, selenides and tellurides (chalcogenides) of molybdenum, tungsten, niobium, tantalum and titanium.
The crystal lattice of graphite consists of hexagonal rings forming thin parallel planes (graphenes). Each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other atoms in the plate (the angle between two bonds is 120°).
The graphenes are bonded to each other by weak Van der Waals forces.
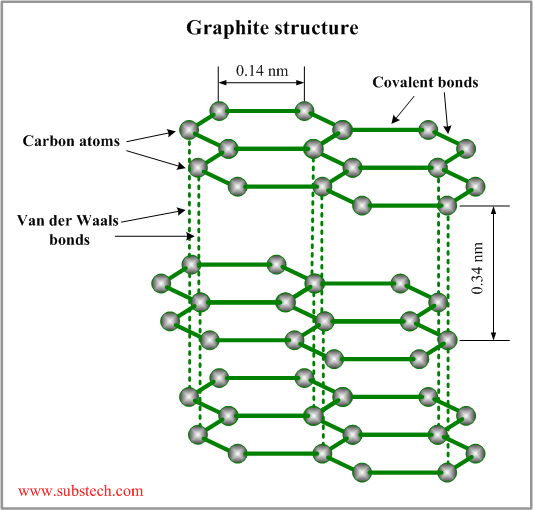
The layered structure allows sliding movement of the parallel planes. Weak bonding between the planes provides low shear strength in the direction of the sliding movement but high compression strength in the direction perpendicular to the sliding movement.
Friction forces cause the graphite particles to orient in the direction, in which the graphenes are parallel to the sliding movement. The anisotropy of the mechanical properties imparts the combination of low coefficient of friction and high carrying load capacity to graphite.
Graphite forms a lubrication film strongly adhered to the substrate surface. The lubrication film provides good wear resistance and seizure resistance (compatibility).
Lubricating properties of graphite are highly dependent on the presence of water vapor in the ambient atmosphere. Water molecules are absorbed on the graphite surface causing further reduction of the bonding between the graphene planes.
Coefficient of friction of graphite in a moist atmosphere is as low as 0.07.
Coefficient of friction of graphite in dry atmosphere or in vacuum reaches 0.5.
Application of graphite as solid lubricant in open air at elevated temperatures is limited to 900°F (482°C). Higher temperatures cause oxidation of graphite and increase of its coefficient of friction.
Some applications of graphite as solid lubricant:
- Carbon brushes including copper-graphite and silver-graphite impregnated composites
- Components of polymer based composite anti-friction coatings
- Second phase particles of metal based composite anti-friction coatings
- Solid lubricant in metal forming
- Bronze-graphite composites for sliding bearings
- Release coatings and non-sticking refractory linings in foundry
Related internal links
to Fluids
to Lubricants


