to Ceramics
to Fundamentals of ceramics
Structure of ceramic materials
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
The following factors affect structure of ceramics:
- Balance of electrical charges of anions and cations
- Radius Ratio (rc/ra)
Where
rc – radius of cation;
ra – radius of anion.
Radius Ratio determines Coordination Number (CN)– the maximum number of anion nearest neighbors for a cation.The anion neighbors do not touch each other.
rc/ra = 0.225…0.414(SiO2) CN = 4
rc/ra = 0.414…0.732(SnO2, PbO2) CN = 6
rc/ra = 0.732…1.0(ThO2) CN = 8
Covalent bonding component, which tends to form tetrahedral coordination, may affect the Coordination Number.
- Ions are packed with maximum density, providing minimum energy of the structure.
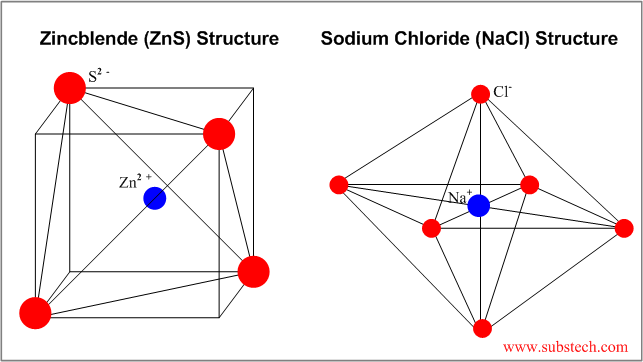
Ceramic structures are classified and designated according to the pattern structures of several natural minerals:
| Mineral Name | Formula | Coordination Number | Structure Characterization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rocksalt | NaCl | 6 | Octahedral unit cell, cubic appearance |
| Zincblende | ZnS | 4 | FCC unit cell with S2- anions at 4 tetrahedral sites |
| Fluorite | CaF2 | 8-cation CN 4-anion CN | FCC unit cell with F- anions at 8 tetrahedral sites |
| Corundum | Al2O3 | 6-cation CN 4-anion CN | HCP unit cell with O2- anions at the lattice sites and Al3+ at interstitial sites |
| Perovskite | CaTiO3 | 6-cation(Ti) CN 2-anion(O) CN | Cubic unit cell with Ti4+ cations coordinated octahedrally among six oxygen anions |
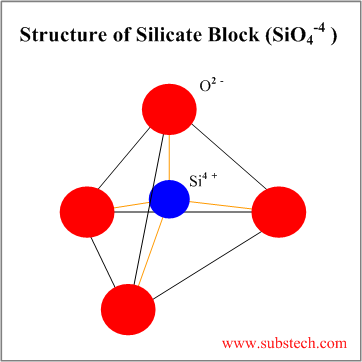
| Silicate | Combination of SiO44- blocks | 4 | Tetrahedral arrangement with Si4+ cations at the center bonded to O2- anions at the apices of the tetrahedron |
Examples of some ceramic structures
Tetrahedral silica block (SiO4-4) may form various silicate structures:
- Island and DoubleIsland Silicates
Single or two silica blocks, containing other cations, form Island (olivine) or Double Island Silicates (hemimorphite).
- Ring and Chain Structures
Several (3,4,5,6) silica units join each other, forming a chain (orthopyroxenes, clinopyroxenes, asbestos) or closed ring (beryl).
- Sheet (layer) structure
Silica units connect to each other, forming infinite sheet (micas, serpentine, chlorite, talc).
- Framework silicate
Quartz, cristobalite, and tridymite minerals are based on the framework silicate structure.
Silicates exist in two forms: crystalline and amorphous (glasses).
to top