Main page
About us
Sliding Bearings Consulting
Advertising Opportunities

to Metals
to Metal forming technologies
Forging
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
Forging is a compressive metal forming process, involving shaping a metal piece by hammer, press or rolls.
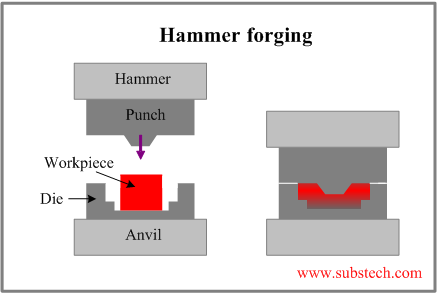
- Hammer forging (drop forging) is forming a preheated workpiece by using impact energy of the falling hammer forcing the metal to fill the space between the punch (a part attached to the hammer) and the forging die (a part attached to the anvil).
- Press forging is forming a preheated workpiece by using a force created by a hydraulically driven ram causing the metal to be squeezed into the die cavity by the static pressure.
Press forging achieves more uniform internal structure due to transmitting deformation to the interior layers of the worpiece. This effect is particularly important when large shafts or other thick parts are forged.
- Upset forging is a forging operation which is employed for manufacturing head of bolts, valves, artillery shells and other parts where increase of cross section dimensions of the workpiece is desired.
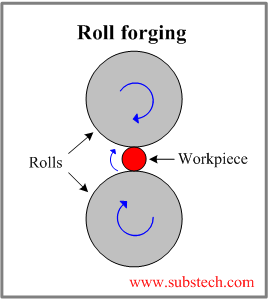
- Roll forging is a forging operation involving reduction of the workpiece diameter (with increase of its length) by rolling it between two grooved rolls rotating at the same rotating direction.
Forging structure is a result of breaking coarse cast structure and forming at first stage grain structure having fibrous character with elongated grains oriented in the direction of the forging stresses. The fibrous grain structure is then converted to the fine equiaxed grain structure (recrystallization process).
Small shrinkage and gas pores are closed up in the hot forging operation, non-metallic inclusions break up and distribute more uniformly.
As a result mechanical properties and homogeneity of the forged parts are improved.
to top
Related internal links