Main page
About us
Sliding Bearings Consulting
Advertising Opportunities

to Metals
to Foundry technologies
Sand casting
Dr. Dmitri Kopeliovich
Sand casting is a method involving pouring a molten metal into a sand mold.
Advantages and disadvantages of sand casting
Advantages of sand casting
- Low cost of mold materials and equipment.
- Large casting dimensions may be obtained.
- Wide variety of metals and alloys (ferrous and non-ferrous) may be cast (including high melting point metals).
Disadvantages of sand casting
- Rough surface.
- Poor dimensional accuracy.
- High machining tolerances.
- Coarse Grain structure.
- Limited wall thickness: not higher than 0.1”-0.2” (2.5-5 mm).
Sand casting mold
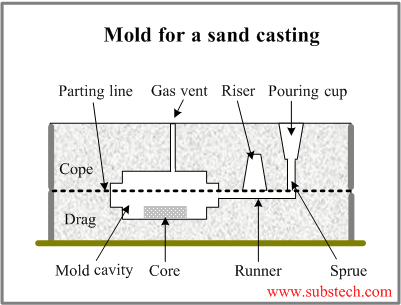
The typical mold for a sand casting is shown in the picture:
The set of channels through which a molten metal flows to the mold cavity is called gating system.
Typical gating system consists of a pouring cup and a sprue receiving the poured melt, runner – a channel through which the melt is supplied to the gates through which the molten metal enters the mold cavity.
A gating system may include a riser (feed head) – a cavity connected to the gating system feeding the casting when it is shrinking.
Air within the mold cavity and gases formed when a molten metal contacts the mold surface are removed through the vents.
The interior cavities of a casting are formed by a separate inserts called cores.
Cores are usually made of sand and backed.
A mold frame (flask) consists of two parts: cope (the upper part) and drag (the lower part).
A mold cavity is formed in the process of pattern molding, when the pattern (commonly wooden) is embedded in sand in the flask forming an impression of the casting.
After the sand packing the pattern is removed from the flask and the cores and the gating system are arranged.
Cores, runner and gates are arranged in the drag; pouring cap and sprue are placed in the cope.
Then the two parts of the mold are assembled and poured.
After the metal has solidified and cooled to a desired temperature, the casting is removed from the mold by the process called shakeout.
to top
Types of sand used for sand casting
Factors determined by sand:
- Casting surface finish.
- Gas permeability of the mold.
- Mold strength.
Requirements to sand:
- Ability to retain mold shape during packing and pouring.
- High temperature stability.
- Permeability for the gases liberated from the mold and solidifying metal.
- Collapsibility - ability of the sand to be shake out.
Silica sand with additives is used for sand casting.
Types of sand:
- Green sand - a mixture of silica sand (quartz) with 4-15% of a clay (bonding agent), about 5% of water and some other additives (iron silicates, zircon, chromites). The green sand is prepared from silica sand, water and a certain quantity of a clay (bentonite, kaolin). Green sand is the most popular sand type.
- Resin bonded sand - a mixture of silica sand with a polymeric resin as the bonding agent. If the resin hardens at room temperature the mixture is called “no bake”.
- Sodium silicate bonded sand - a mixture of silica sand with 3-4% of sodium silicate (waterglass, NaO*nSiO2*mH2O). The bonding forms when sodium silicate reacts with CO2, which is applied to the mixture: NaO*nSiO2 + CO2 = Na2CO3 + SiO2. The mixture is called “no bake” since the binding process does not require heat treatment (baking). Sodium silicate bonded sand is widely used for the preparation of cores. The main disadvantage of sodium silicate bonded sands is their bad collapsibility.
Patterns for sand casting
In order to be used repeatedly patterns are made of relatively tough materials.
Patterns materials:
- Wood
- Metal
- Plastic
- 3D Rapid Prototype printing
A parting (release) agent is applied on the pattern surface in order to provide easy removal of the pattern from the mold.
Patterns may be made as one-piece or multiple-piece (split, match plate).
Patterns are commonly made larger than the casting because of the shrinkage effect.
Shrinkage allowances are usually 1-2%.
The pattern surfaces are never made perpendicular to the mold parting surface. The taper of the pattern surface, which provides narrowing the mold cavity towards the mold parting surface is called draft.
Draft allows easy removal of the pattern and the casting from the sand mold.
The draft angle is commonly 1-3%.
to top
Related internal links
to Metals
to Foundry technologies